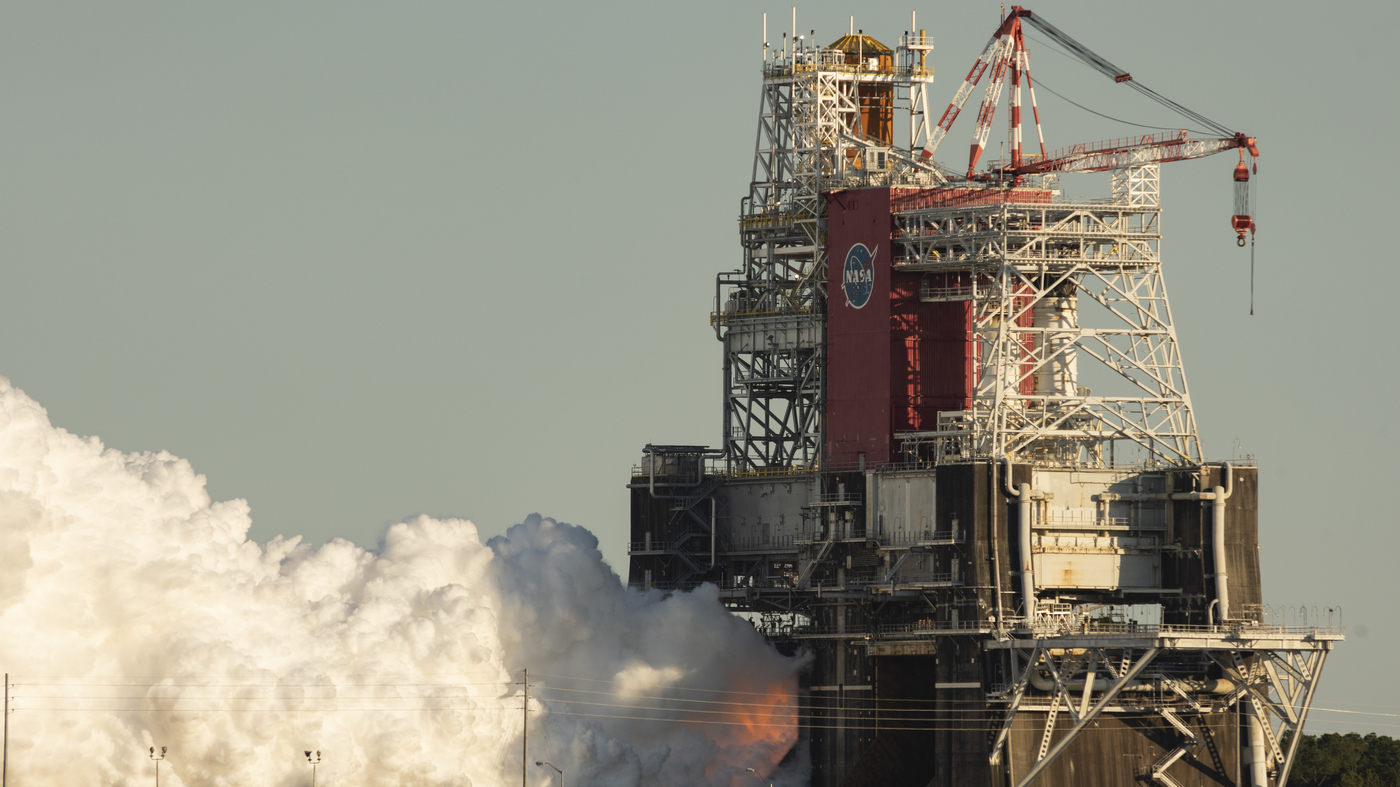
In this image provided by NASA, the base stage of the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System missile is seen at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four engines fired for a little over a minute.
NASA / Getty Images
Hide the caption
Toggle caption
NASA / Getty Images
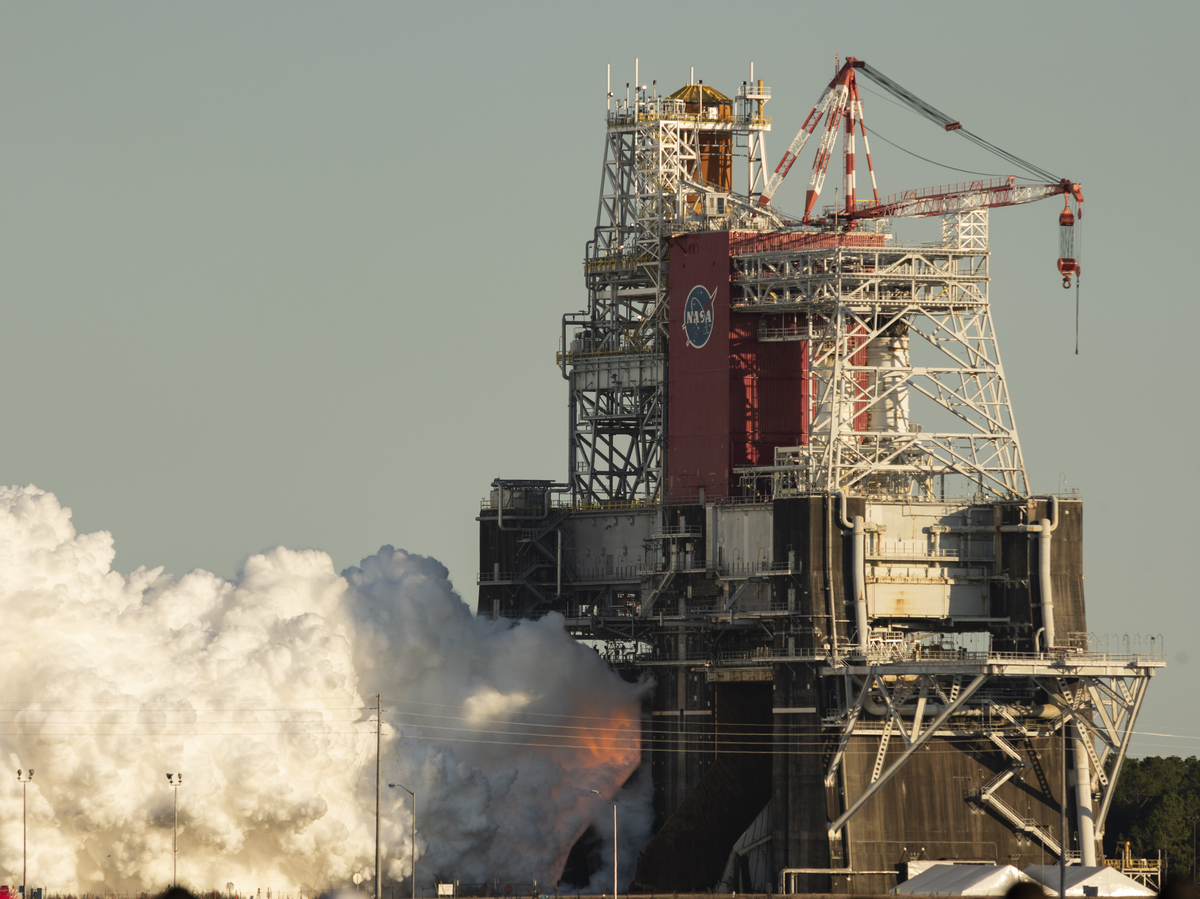

In this image provided by NASA, the base stage of the first flight of NASA’s Space Launch System missile is seen at NASA’s Stennis Space Center near Bay St. Louis, Mississippi. The four engines fired for a little over a minute.
NASA / Getty Images
NASA has more work to do, after it finished testing a missile on Saturday to replace the shuttle with a premature and unexpected shutdown.
The test, at NASA’s Stennis Space Center in Mississippi, was part of NASA’s Artemis Program, a plan Return to the moon In the coming years. NASA’s test called for four engines to launch for eight minutes – roughly the time it would take for NASA’s Space Launch System (SLS) to generate the thrust needed to send the rocket into space.
But the engines stopped after only 67 seconds, when the No. 4 engine suffered.Major component failure. Scientists are not yet sure what caused the early lockdown, but they plan to analyze and regroup.
“The Saturday test was an important step forward to ensuring that the base stage of the SLS missile was ready for the Artemis I mission, and for carrying the crew on future missions,” said NASA Administrator Jim Bridenstine, who attended the test.
“Even though the engines did not fire for the full duration, the team worked successfully during the countdown and ignited the engines and gained valuable data to inform our path forward,” he said.
The same engines NASA tested will be used to launch the Orion space capsule to the moon. So scientists should be careful with them.
“The amount of risk we can take is very low,” said Bridenstein. “We cannot afford this car’s failure. And guess what? Because we did all the work we did, this article made the right decision to shut itself down.”
Well, the MCF wasn’t a call this boarding flight manager wanted to hear: Major component failure detected by the SSME controller.
– Wayne Hale (@waynehale) January 16, 2021
Now NASA has to figure out what caused the component failure that led to the shutdown. If the scientists do another test, it will take at least 3-4 weeks to get the engines ready, the agency said.
NASA announced the SLS about 10 years ago, the successor to the retired Space Shuttle program. It is a rocket and capsule combination that, when completed, will enable deep space missions. NASA hopes to have astronauts on the moon in 2024, and eventually Mars And beyond.

“요은 베이컨과 알코올에 대한 전문 지식을 가진 닌자입니다. 그의 탐험적인 성격은 다양한 경험을 통해 대중 문화에 대한 깊은 애정과 지식을 얻게 해주었습니다. 그는 자랑스러운 탐험가로서, 새로운 문화와 경험을 적극적으로 탐구하며, 대중 문화에 대한 그의 열정은 그의 작품 속에서도 느낄 수 있습니다.”