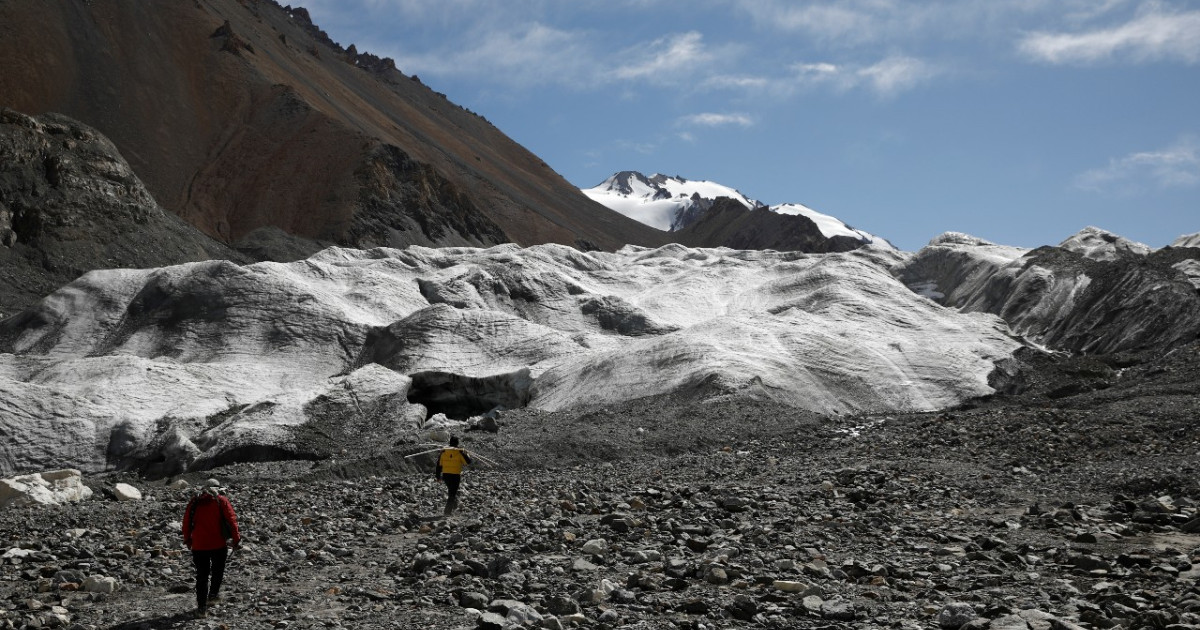
The rate of loss increased from 0.8 trillion tons per year in the 1990s to 1.3 trillion tons per year by 2017, with potentially dire consequences.
British scientists have warned in new research that the rate of ice disappearance around the world matches the “worst-case scenario of climate warming.”
A team from the universities of Edinburgh, Leeds and University College London said that the rate of melting of snow in the polar regions and mountains of the world has increased significantly in the past 30 years.
Using satellite data, experts found that the Earth lost 28 trillion tons of ice between 1994 and 2017.
They said the rate of loss rose from 0.8 trillion tons per year in the 1990s to 1.3 trillion tons per year by 2017, with potentially dire consequences for people living in coastal areas.
“Ice sheets are now pursuing the worst-case warming scenarios developed by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC),” said Thomas Slater, a research fellow at the University of Leeds’ Center for Polar Observation and Modeling.
“Sea level rise at this scale will have very serious impacts on coastal communities this century.”
The contribution of the United Nations’ Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change has been critical in shaping international climate change strategies, including the 2015 Paris Agreement in which the majority of countries that emit greenhouse gases agreed to take steps to mitigate the impact of global warming.
The university research, published in the European Union’s Journal of Geosciences The Cryosphere, was the first of its kind to use satellite data.
It surveyed 215,000 mountain glaciers around the world, polar ice sheets in Greenland and Antarctica, floating ice shelves around Antarctica and drifting sea ice in the Arctic and the Southern Ocean.
Losses at the Arctic, Antarctic
The survey found that the biggest losses in the past three decades were from Arctic sea ice and Antarctic ice shelves, both of which are floating on the polar oceans.
While this ice loss does not directly contribute to sea rise, its destruction stops the ice sheets reflecting solar radiation and thus contributes indirectly to rising sea levels.
“As sea ice shrinks, the oceans and the atmosphere absorb more solar energy, causing the Arctic to warm faster than anywhere else on the planet,” said Isobel Lawrence.And the Research fellow at the University of Leeds
“Not only does this accelerate the melting of sea ice, but it also exacerbates melting of glaciers and ice sheets, which leads to rising sea levels,” she added.
A previous study published in the US-based Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences Journal estimated that global sea levels could rise by two meters (6.5 feet) by the end of this century due to global warming and greenhouse emissions.
The report also stated that in the worst-case scenario, global temperatures would rise by more than five degrees Celsius (nine degrees Fahrenheit), causing waters to rise and displace millions of people who live in coastal areas.
Another study, published by the Central Climate Center in the United States in 2019, said that up to 300 million people could be affected by devastating floods by 2050, nearly three times what was previously expected. The number could rise to 630 million by 2100.
The study warned that major coastal cities such as Mumbai, India, Shanghai, China, and Bangkok, Thailand, may be submerged in water over the next 30 years.
The research said that an estimated 237 million people threatened by rising sea levels live in Asia alone.

“요은 베이컨과 알코올에 대한 전문 지식을 가진 닌자입니다. 그의 탐험적인 성격은 다양한 경험을 통해 대중 문화에 대한 깊은 애정과 지식을 얻게 해주었습니다. 그는 자랑스러운 탐험가로서, 새로운 문화와 경험을 적극적으로 탐구하며, 대중 문화에 대한 그의 열정은 그의 작품 속에서도 느낄 수 있습니다.”