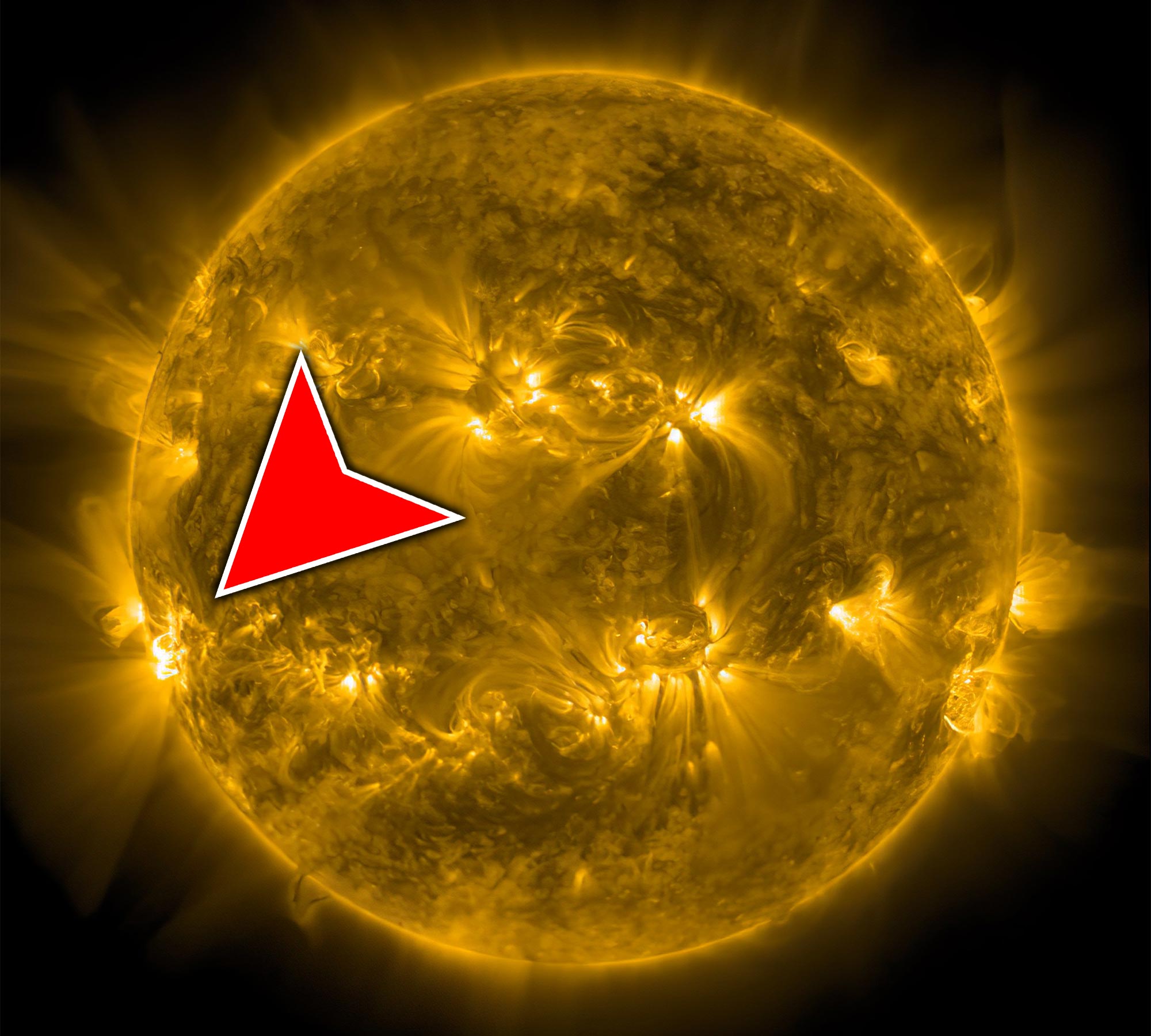
2023년 6월 20일, 태양은 NASA의 Solar Dynamics Observatory에서 포착한 강력한 태양 플레어를 방출했습니다. 크레딧: NASA/SDO
태양은 오후 1시 9분에 정점에 달하는 강력한 태양 플레어를 방출했습니다.[{” attribute=””>EDT on June 20, 2023. NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory, which watches the Sun constantly, captured an image of the event.
A solar flare is a sudden, significant increase in brightness observed near the sun’s surface, typically around a sunspot group. They are a violent eruption of high-energy particles and gases that are ejected from the sun’s magnetic field into space. Solar flares release a lot of energy, ranging from the equivalent of ten million hydrogen bombs to a billion hydrogen bombs.
This flare is classified as an X1.0 flare. X-class denotes the most intense flares, while the number provides more information about its strength.
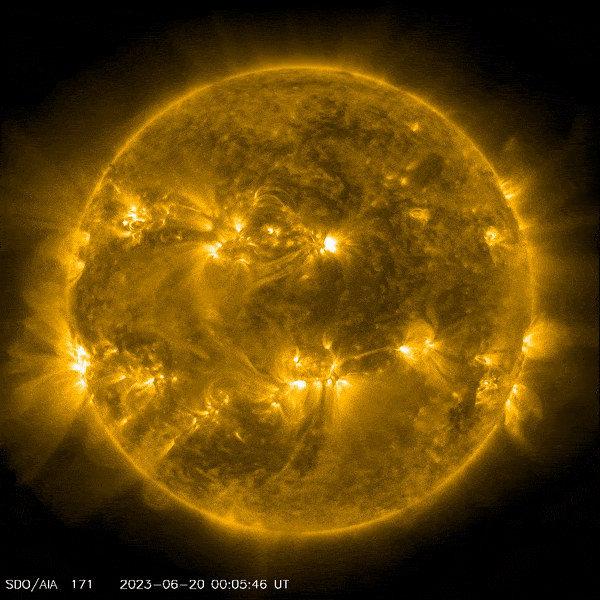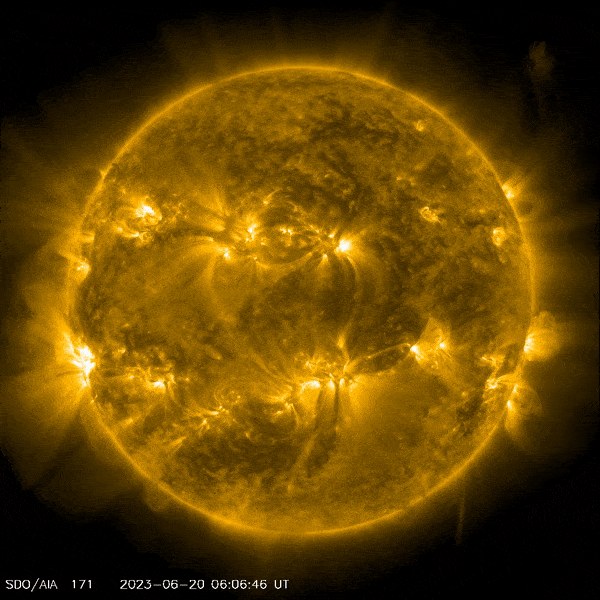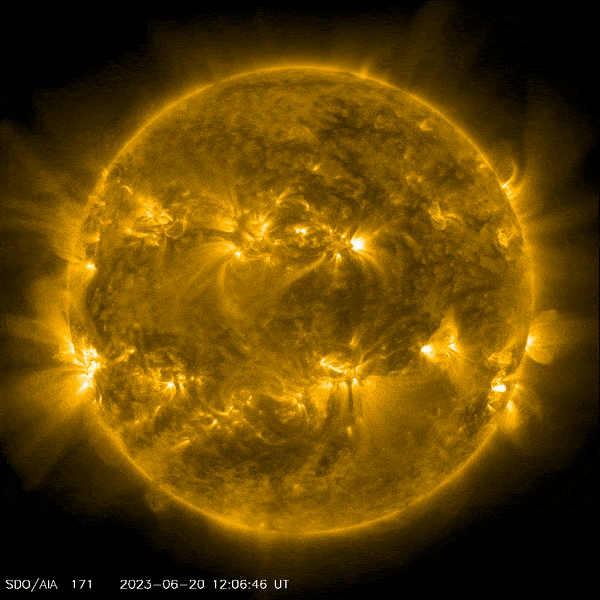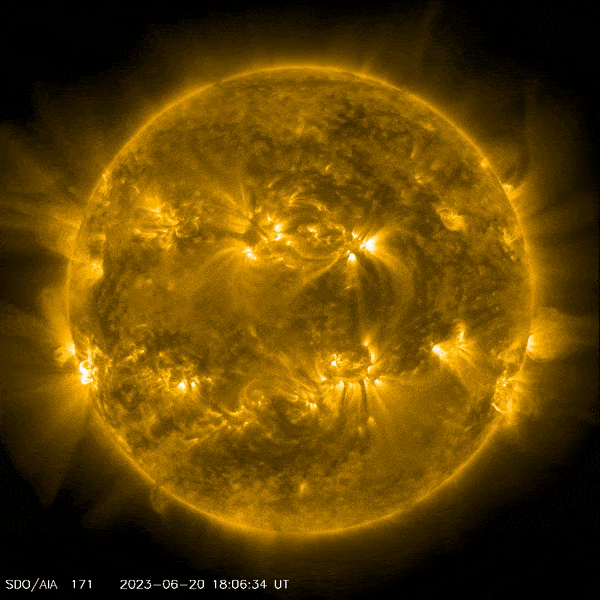
NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory captured this image of a solar flare – as seen in the bright flash on the lower left – on June 20, 2023. The image shows a subset of extreme ultraviolet light that highlights the extremely hot material in flares, and which is colorized in yellow. Credit: NASA/SDO
How are Solar Flares Measured
Solar flares are measured in terms of their x-ray intensity in the Earth’s vicinity. The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA) classifies solar flares in three categories:
- X-class flares: These are big; they are major events that can trigger planet-wide radio blackouts and long-lasting radiation storms.
- M-class flares: These are medium-sized; they can cause brief radio blackouts that affect Earth’s polar regions. Minor radiation storms sometimes follow an M-class flare.
- C-class flares: These are small, with few noticeable consequences here on Earth.
Each class has a tenfold increase in intensity from the last, so an X is ten times an M and 100 times a C.
Effects of Solar Flares on Earth
Solar flares can have a wide range of effects on Earth. Here are a few:
- Radio Communication Disruption: When solar flares interact with the Earth’s atmosphere, they can cause disturbances in the Earth’s magnetic field, which can interfere with radio and GPS signals, causing blackouts and navigation issues.
- Geomagnetic Storms & Aurora: If the solar flare is accompanied by a coronal mass ejection (CME), a massive burst of solar wind and magnetic fields released into space, it can lead to geomagnetic storms. These storms can induce electric currents in power grids, potentially causing power outages. However, they can also create stunning auroras (Northern and Southern Lights).
- Radiation Risk: Solar flares produce high levels of radiation that can pose a risk to astronauts in space or passengers in high-altitude flights. They’re also a concern for electronic systems on satellites and spacecraft.
- Effect on Satellites: The high-energy particles from a solar flare can damage satellites, leading to malfunctions or loss of data.
It’s important to note that Earth’s magnetic field and atmosphere protect humans on the ground from the harmful effects of solar flares; most of the concern is for space-borne technology and astronauts. However, in the event of a particularly strong solar flare, the consequences could be more severe. That’s why space weather monitoring organizations keep a close watch on solar activity.

Artist’s concept of the Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO). Credit: NASA/Goddard Space Flight Center Conceptual Image Lab
NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory
NASA’s Solar Dynamics Observatory (SDO), launched in February 2010, is a mission dedicated to studying the Sun. It’s designed to help us understand the Sun’s influence on Earth and near-Earth space by studying the solar atmosphere on small scales of space and time and in many wavelengths simultaneously.
SDO’s primary goals are:
- Solar Interior Dynamics: To understand the solar interior and how the Sun’s magnetic field is generated and structured. It uses helioseismology, studying the oscillations in the sun, to map the interior of the sun.
- Magnetic Field: To understand how the Sun’s magnetic field is released into the heliosphere (the space around the Sun) and geospace in the form of solar wind, energetic particles, and variations in the solar irradiance.
- Solar Energy Release: To understand the sources of solar variability that influence life and society by studying how magnetic energy is converted to the kinetic energy of solar wind, radiant energy of light and heat, and magnetic energy in solar flares and mass eruptions.
The SDO includes a suite of instruments:
- Helioseismic and Magnetic Imager (HMI): It studies oscillations and magnetic fields at the solar surface, or photosphere.
- Atmospheric Imaging Assembly (AIA): It images the solar atmosphere in multiple wavelengths to link changes in the surface to interior changes. Its data includes images of the Sun in 10 wavelengths every 10 seconds.
- Extreme Ultraviolet Variability Experiment (EVE): It measures the Sun’s ultraviolet brightness, an important energy source that affects the Earth’s atmosphere and climate.
SDO is one of the missions in NASA’s Living With a Star (LWS) Program, which aims to understand the aspects of the Sun and the Earth’s space environment that affect life and society. The SDO data, continuously streaming down to Earth in near-real time, has transformed our understanding of the Sun and its effects on our planet.

“요은 베이컨과 알코올에 대한 전문 지식을 가진 닌자입니다. 그의 탐험적인 성격은 다양한 경험을 통해 대중 문화에 대한 깊은 애정과 지식을 얻게 해주었습니다. 그는 자랑스러운 탐험가로서, 새로운 문화와 경험을 적극적으로 탐구하며, 대중 문화에 대한 그의 열정은 그의 작품 속에서도 느낄 수 있습니다.”